
Children from low-income households are
increasingly being segregated into different classrooms from their peers from higher-income households, according to recent research
I have conducted with education policy scholar
Dave E. Marcotte.
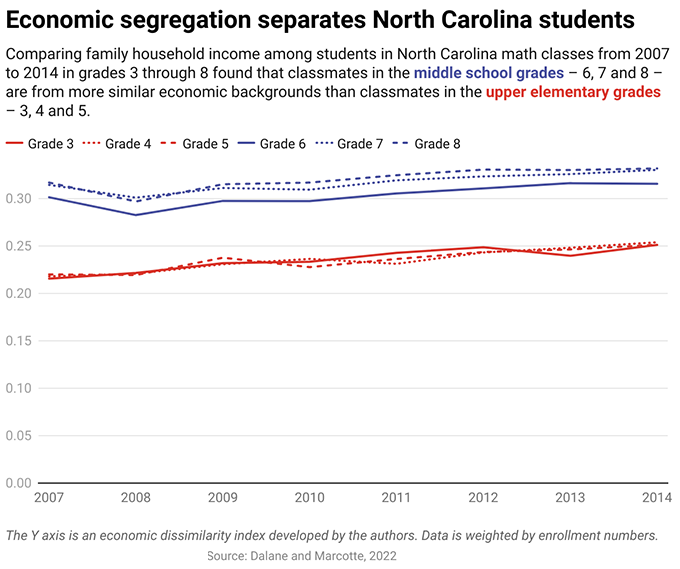
From 2007 to 2014, we tracked all North Carolina public school students statewide, from third through eighth grades, observing how the students were grouped into math and English language arts classes by each school’s process for creating class groups.
We used course enrollment data to figure out how many students in each classroom were from families whose incomes are at or below 185% of the federal poverty threshold – and how many were not. We found that those economically disadvantaged students were increasingly likely to be concentrated in a subset of classrooms rather than spread out relatively evenly throughout the school.
Why it matters
Often school segregation is thought about as Black and white students being forced to attend
different schools. This makes sense given the
history of Jim Crow – a 19th- and 20th-century legal system meant to
relegate Black people to second-class status in white society – and
court orders to desegregate schools.
Another aspect of this issue is how students are sorted into classrooms within schools. A 2021 study found that more racially diverse schools are
more likely to have classrooms that are more segregated than schools that are less diverse overall.
Researchers have recently begun to identify
rising levels of segregation between schools based not just on race, but also on household income.
Students from wealthier households are more likely than their less-well-off peers to have
higher academic achievement as measured by test scores and to
attend and complete college.
Efforts to provide equitable opportunities for all students often focus on comparing funding and staffing between schools. Indeed, lower levels of school funding lead to
lower educational attainment and lower wages in adulthood.
However, resources can also be distributed inequitably within schools, on a classroom-by-classroom basis. For instance,
more experienced teachers raise student test scores more than novice teachers, on average. However, novice teachers are
frequently assigned to classrooms with more low-income students. Therefore, the more students are separated along lines of household income, the more likely poorer students are to fall behind academically.
What still isn’t known
We aren’t sure why there is an increase in segregation within schools by household income. One potential reason could be an increase in what is called “
academic tracking,” which is the process of grouping students into classes based on their prior achievement, such as performance on standardized tests.
If
low-income students perform worse on standardized tests than their peers, they may be placed in lower tracks. However, standardized test scores may not accurately reflect ability for low-income students, since
students from marginalized groups perform disproportionately worse on assessments.
If in fact test scores do accurately reflect ability, there may be
some educational advantages to track students into certain classes. However, researchers have long argued that
tracking perpetuates inequalities between low- and high-tracked students. For example, students who are placed on lower tracks than their peers
suffer from lower self-esteem and are
not as well prepared for college success as higher-tracked students with similar test scores.
The
growth in charter school enrollments over the past two decades could also contribute to the increases in within-school segregation by income that we find. Public school principals who fear their students may depart for charters may attempt to retain them
by introducing specialized curricula or expanding gifted and talented programs. If these programs continue to primarily serve students from families with higher incomes, that could increase income segregation within schools. This is a possibility we are exploring.
Author Bio: Kari Dalane is a Ph.D. Candidate in Public Administration and Policy at the American University School of Public Affairs
 Children from low-income households are increasingly being segregated into different classrooms from their peers from higher-income households, according to recent research I have conducted with education policy scholar Dave E. Marcotte.
From 2007 to 2014, we tracked all North Carolina public school students statewide, from third through eighth grades, observing how the students were grouped into math and English language arts classes by each school’s process for creating class groups.
We used course enrollment data to figure out how many students in each classroom were from families whose incomes are at or below 185% of the federal poverty threshold – and how many were not. We found that those economically disadvantaged students were increasingly likely to be concentrated in a subset of classrooms rather than spread out relatively evenly throughout the school.
Children from low-income households are increasingly being segregated into different classrooms from their peers from higher-income households, according to recent research I have conducted with education policy scholar Dave E. Marcotte.
From 2007 to 2014, we tracked all North Carolina public school students statewide, from third through eighth grades, observing how the students were grouped into math and English language arts classes by each school’s process for creating class groups.
We used course enrollment data to figure out how many students in each classroom were from families whose incomes are at or below 185% of the federal poverty threshold – and how many were not. We found that those economically disadvantaged students were increasingly likely to be concentrated in a subset of classrooms rather than spread out relatively evenly throughout the school.
